
IELTS WT1 (Process Diagram)
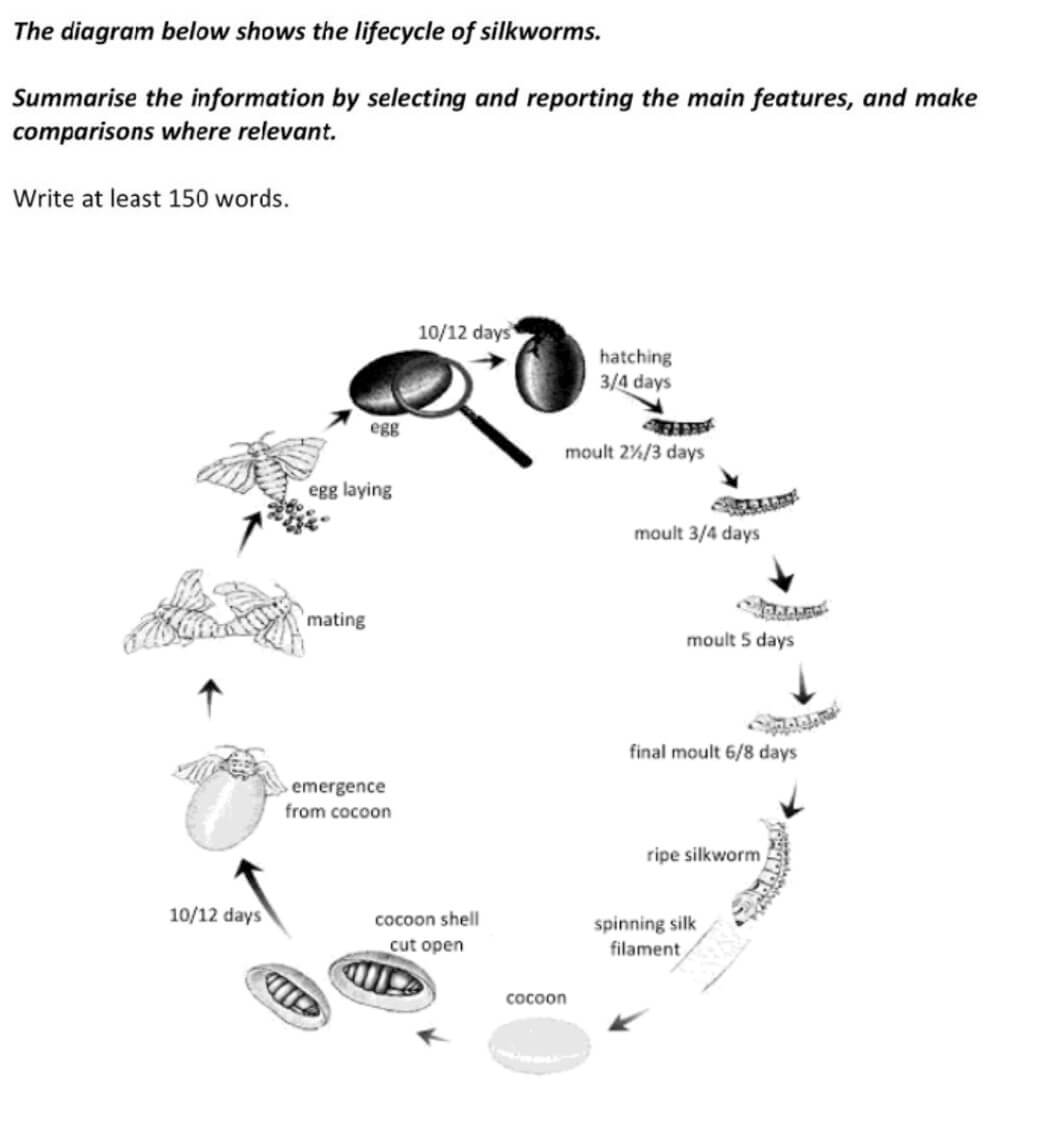
The supplied illustration demonstrates the lifecycle of a silkworm.
Overall, it is clear that the lifecycle is a natural process and contains 12 cyclical phases, beginning with mating of two silkworms and ending with the birth of a new one from a cocoon.
The process commences with two silkworms mating and then laying eggs. It takes 10-12 days for eggs to begin hatching which continues next 3 or 4 days. After newborn silkworm hatches, it starts to moult. There are altogether 4 molts in silkworm’s life. First one takes from 2 and a half to 3 days, second — from 3 to 4 days. Third and final fourth molts continue for 5 and 6-8 days respectively.
Once silkworm goes through its last molt, it becomes a ripe silkworm that is ready to make a cocoon. Silkworm constructs it out of spinning silk filament. Once silkworms finish the cocoon, it gets cut open. In the final stage, silkworm emerges from this open cocoon and the process starts over.
by Zhanel Dorzhigulova
You should spend about 20 minutes on this task. The diagram illustrates the process that is used to manufacture bricks for the building industry. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant. Write at least 150 words.
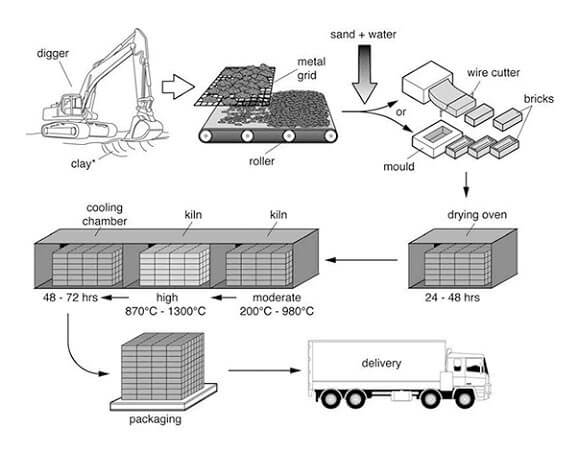
The process diagram depicts the production of bricks which are utilised for the construction industry.
Overall, the given linear process of bricks manufacture includes six stages. It begins with digging of clay as a raw material and finally results in bricks being shipped.
First of all, an excavator digs out the clay, which is then broken up using a metal grid and a roller into homogeneous texture. In the next step, crushed clay is mixed with other raw materials such as sand and water. After that, to obtain the appropriate shape of brick, the mixture is processed via either a wire cutter or a mould.
Following that, as the generated brick is still wet, it should be placed in oven for 1-2 days to be dried. The drying procedure continues using a kiln at moderate, up to 980 degrees Celsius and high temperatures up to 1300°. This step also consists of chamber which cools down the bricks for 2-3 days. This process of making bricks ends with their packaging and consequently delivering to the building industries.
by Gulmira Kinzhekeyeva
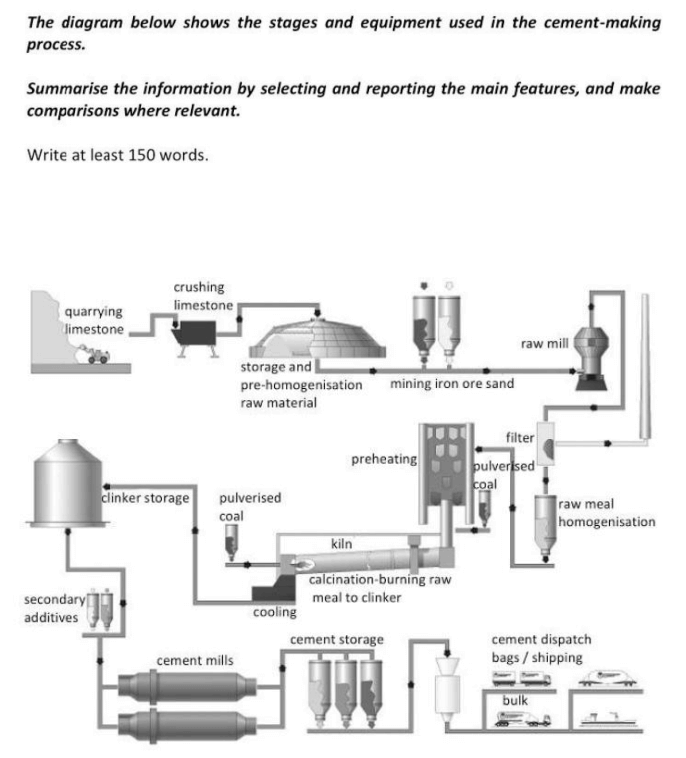
The supplied illustration demonstrates how cement is made and what kind of equipment is required for it.
Overall, it is a 15 stage, man-made, linear process. It begins with digging limestone and finally results in cement being delivered.
First of all, an excavator quarries limestone that later will be crushed. Then the raw material is stored in order to be pre-homogenised. After this, an iron ore sand is mined and goes through raw mill, then through filter and raw meal homogenisation. The product goes to preheating with pulverised coal. Next is kiln, where raw meal is calcination-burned to clinker. Then clinker is mixed with pulverised coal again and goes to cooling section.
Following that, cooled mix goes to clinker storage, where it gets separated in secondary additives, which later will go through cement mills. After material becomes cement, it goes to cement storage. From this, cement gets packed in dispatch bags and shipped.
by Zhanel Dorzhigulova

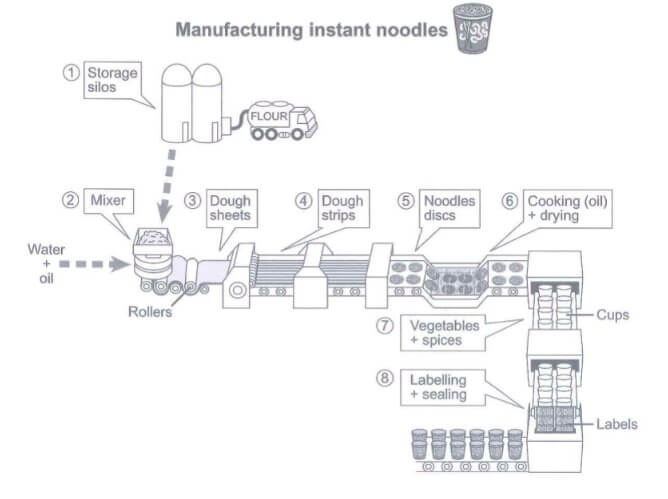
The diagram illustrates the process of making instant noodles. The process is fully automated.
Overall, there are eight steps in instant noodles production starting with storing silos and finishing with labeling and sealing.
First, floor for noodles is stored in silos and then put in the mixer. Water and oil are added into a mixing machine in order to get dough. Next, dough sheets are produced by rollers that are connected with the mixer. Then, sheets are cut into long dough strips. The following step is to make noodle discs from dough strips by means of an automated system.
Instant noodles are made by cooking dough discs in oil. Before adding vegetables and spices, noodles are dried and placed into numerous of cups. After that, cups go through the labelling process. The last step is sealing labeled instant noodle cups. The product is ready to be stored in the supermarket.
by Daniya Bekentaeva
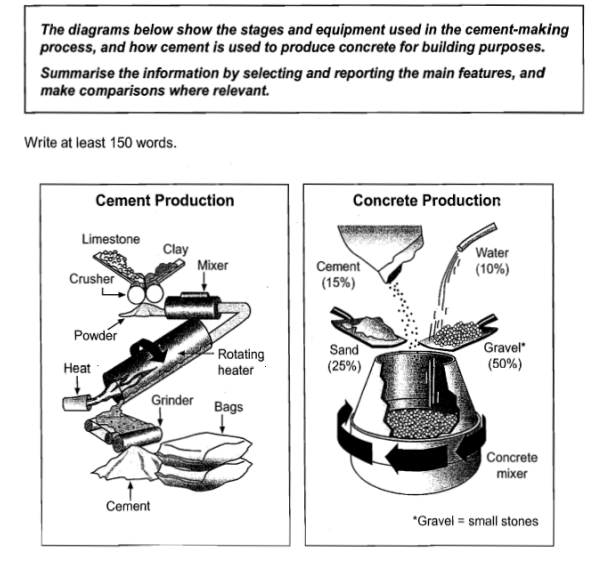
The illustration demonstrates the phases in the manufacture of cement as well as necessary equipment for making it, and the production of concrete using cement.
Overall, first production includes five man-made stages, while second one consists of only one step, however both of them appear to be linear process.
First of all, limestone and clay are crushed and turned into a powder in order to use them as a raw material. After that, the two materials are mixed, which is then sent to be rotated by heat. In the following stage, it needs grinding so it can finally become cement. This process of making cement ends with packing it in bags.
The manufacture of concrete consists of certain percentage of the four raw materials: 15% of cement, 10% of water, 25% of sand and 50% of gravel. They are thoroughly mixed and in the end of the short process concrete is taken.
by Aigerim Bekbolatova
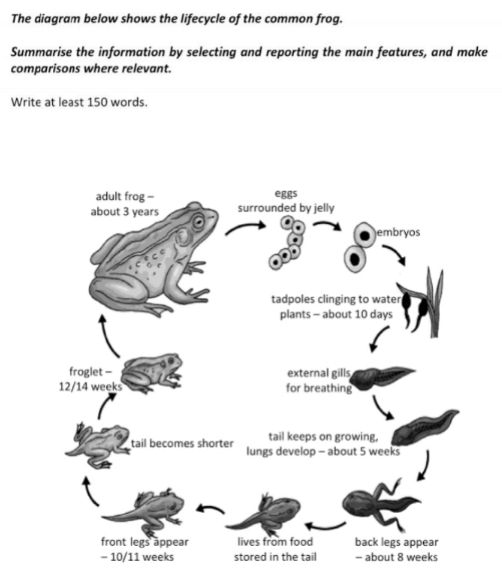
The illustration represents the lifecycle of a frog.
Overall, it is clear that the process of life is a natural one, involving 11 cyclical phases beginning with the emergence of eggs and ending with the maturation of embryos into an adult frog.
The lifecycle commences with adult frog laying eggs that are surrounded by jelly. After embryo creation starts, it takes approximately 10 days for tadpoles to cling to water plants. In the next stage, external gills appear for breathing. In the fifth week, the tail continues to grow, while the lungs develop. Once they start breathing, their back legs appear which takes about 8 weeks.
The next stage in the cycle is when the baby frog’s diet is maintained by the food stored in its tail. On the tenth or eleventh week, the amphibian's front legs appear. Once frog’s all legs are fully developed, its tail becomes shorter, and in 12-14 weeks it becomes a froglet. In the final stage, the froglet emerges as an adult frog and this process takes about 3 years and then the cycle starts over.
by Alua Adenova
The diagram below shows how geothermal energy is used to produce electricity.
Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
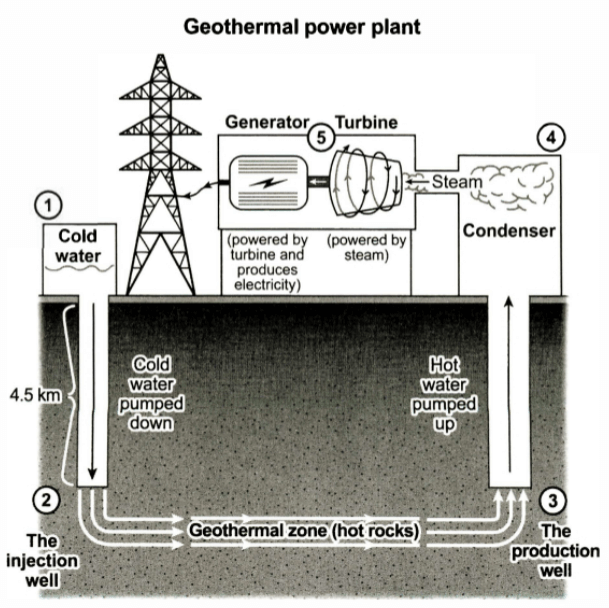
The diagram displays how a geothermal power station generates electricity.
Overall, the station produces electricity in five main steps: pumping cold water underground, heating it, pumping heated water to the surface, converting it into steam, and using the steam to turn the turbine to create electricity.
First of all, cold water stored in the container is pumped down to the injection well that is 4.5 kilometers deep beneath the Earth’s surface. The well then injects the water into the geothermal zone where it is heated by hot rocks.
The superheated water is subsequently pumped above the ground and into the condenser. Here, its pressure is lowered, which turns it into steam. As the steam passes through the turbine, it drives its blades to rotate. The spinning turbine then powers the generator connected to it to create electricity. Finally, the generated electricity is delivered to the power grid through power lines.
by Bekassyl Adenov
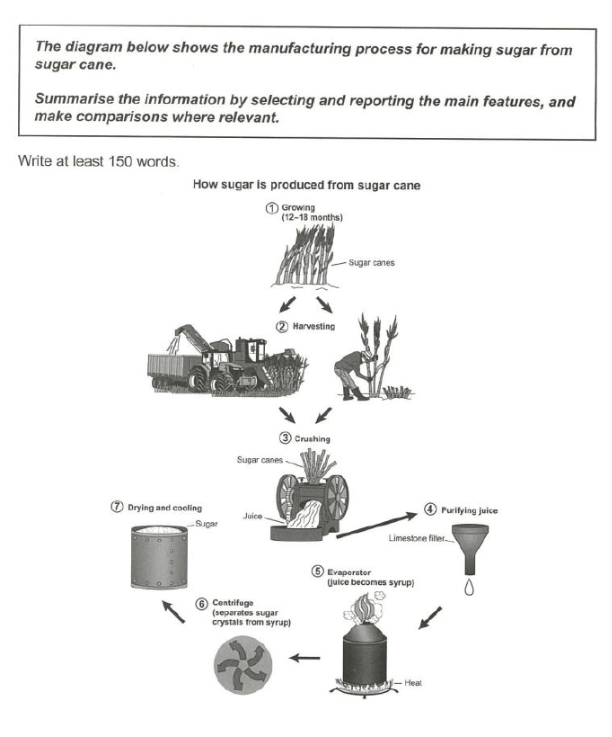
The illustration above gives information about the process of producing sugar from sugar canes.
Overall, it is a 7 stage, artificial, linear process. It begins with growing sugar canes and extracting the juice from them, and ends with drying and cooling the sugar that has been separated from the syrup.
First of all, sugar canes are grown for a period of 12 to 18 months, after which they are gathered either by hand or by harvesting machines. After that, the canes are crushed, so their juice can be extracted, and the limestone filter is used, as it helps to purify the juice.
The following step is evaporating water out of the juice by applying heat, in order to turn it into the syrup. Then, the centrifuge is used, which enables sugar crystals to be separated from the syrup. The last step is leaving the sugar to dry and cool, since the heat, which was used while making the syrup has not gone away yet.
by Nurasyl Tleubekov
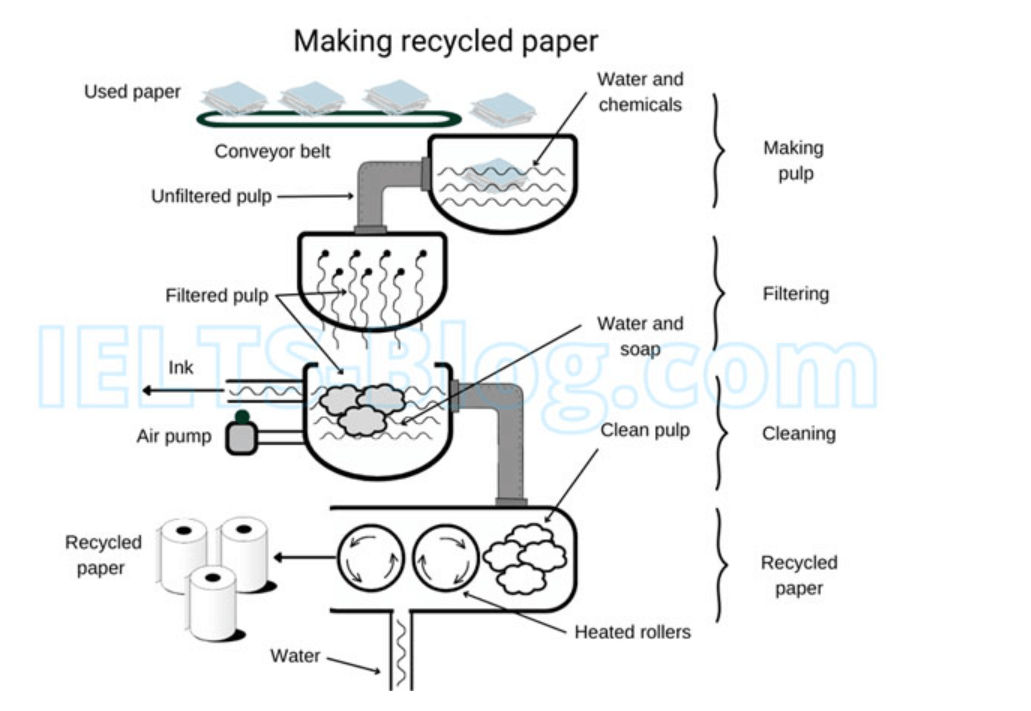
The process diagram demonstrates the steps involved in making recycled paper.
Overall, it is four-stage, artificial, linear process. It begins with making pulp out of used paper and finally results in production of new paper.
In the first stage of the recycling process, all used paper is placed on a conveyor belt for further processing. Following this, paper is transferred to a container with water and chemicals. This mixture breaks paper into pieces and creates the pulp. Created pulp needs to be properly filtered.
After filtration comes the cleaning process. All filtered pulp is put into a container with water and soap. In this stage, air pump and ink are removed to ensure that pulp is as clean as possible. Next, the cleaned and de-inked pulp is heated in rollers and water is taken out. Finally, the heated pulp then rolled into sheets of paper, the end product, which can be recycled again.
by Adina Zhorobekova
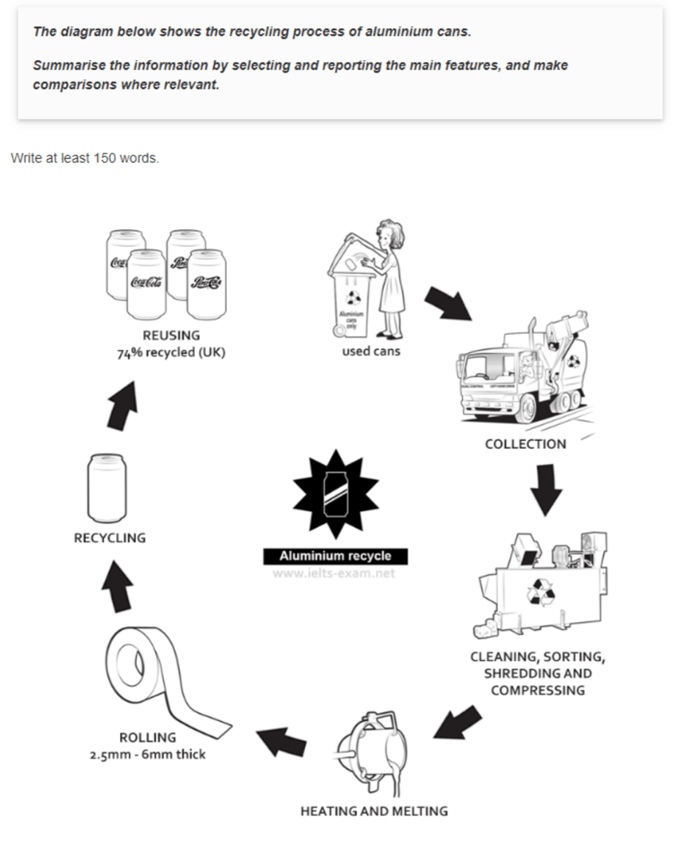
The diagram depicts a sequence of actions on how aluminum cans are recycled, which must be taken by special collection trucks to be driven to a factory to undergo various recycling transformations.
First, the used aluminum cans are collected in recycling bins and then transported to a recycling facility. There, they undergo meticulous cleaning, removing grease and harmful pollutants. After the cleaning procedure, the cans are sorted for recycling eligibility and separated from other trash. Immediately after sorting, the chosen cans can be shredded into small particles and wholly crushed in a machine to shrink in size and be suitable to handle.
When the products are processed, they are melted at a high temperature, transforming them into a molten liquid. The liquid aluminum is then distributed into molds to form thin sheets to make beverage cans. About three-quarters of the cans in the UK can be recycled after use, contributing to a more sustainable environment.
by Alima Almadiyeva
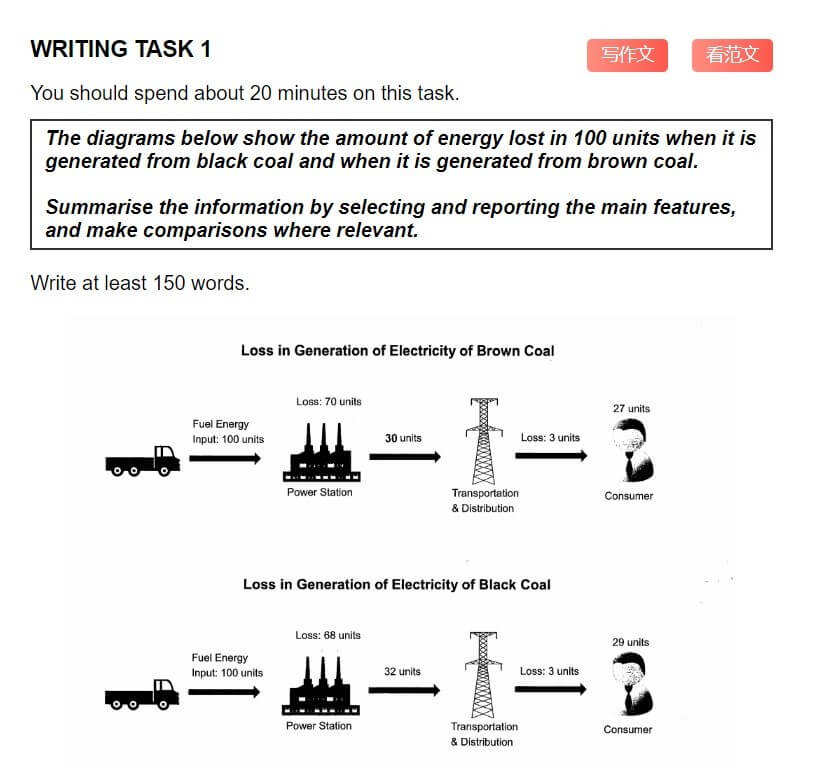
The diagrams illustrate the amount of energy loss during the generation of electricity from brown coal and black coal, based on an initial input of 100 units of fuel energy.
Overall, the diagrams reveal that energy loss is slightly higher when electricity is generated from brown coal compared to black coal.
In the case of brown coal, out of 100 units of fuel energy, 70 units are lost in the power station, leaving only 30 units available for transportation and distribution. During this stage, a further loss of 3 units occurs, resulting in 27 units of electricity reaching the consumer.
For black coal, the loss at the power station is slightly lower, amounting to 68 units. This leaves 32 units for transportation and distribution, where another 3 units are lost. Consequently, 29 units of electricity are delivered to the consumer.
While both processes exhibit significant energy losses, black coal is slightly more efficient, with 2 additional units of electricity reaching the consumer after accounting for all losses. This difference can be attributed to the slightly lower energy loss at the power station during black coal processing.
by Ainel
